Most spiders have eight eyes, but some species have six, four, two, or some eyes. Even within a single species, the number of eyes can vary, but it is always even.
How many Eyes do Spiders Have mostly
- About 99% of spiders have eight eyes. Some come in six, four or two. Some species have no trace of snow at all.
- Spiders have two types of eyes. The car forms an image of a large pair of eyes. The secondary eye helps the spider track move and gauge distance.
- The number and arrangement of spider eyes helps arachnologist to identify the spider species.
Why spiders have many eyes
The spider can refer to the cephalothorax (“head”), which needs so many eyes because it cannot twist . Rather, it is fixed in the eye position. In order to hunt and evade predators, spiders must be able to detect movement around them all.
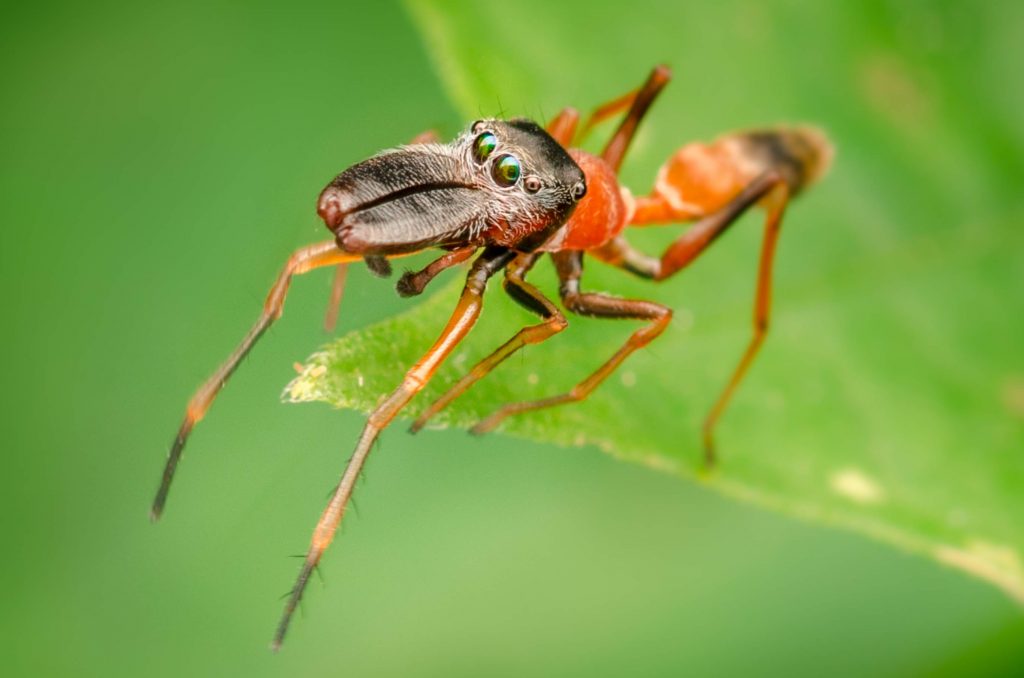

Types of spider eyes
The two main types of eyes are the future-facing primary eye and the secondary eye called ocelli. In other arthropods, ocelli sense the direction of light, but in spiders these eyes form a true image. The main eye contains muscles that move the retina to focus and track the image. Most spiders have poor eyesight, but in ocelli jumping spiders exceed dragonflies (the best visionary insects) and humans approach them. Because of their position, ocelli is known as Ante Media Eye or AME.
Secondary eyes are derived from compound eyes, but they do not have sides. They are generally smaller than tea snow. These eyes lack muscle and move completely. Most primary eyes are round, but some have ovals or half moons. Eyes are classified according to their location. It is the upper row of the eye on the head side of the anterolateral eye (ALE). The lateral eye (PLE) is the second row of eyes on the side of the head. posters-the middle eye (PME) is in the middle of the head. The car may be facing in front of the eye or on the side, top or back of the spider’s head.
The secondary eye serves a variety of functions. In some cases, the lateral eye extends the range of the primary eye giving a wide-angle image to the arachnid. The secondary eye acts as a motion detector and provides depth perception information that helps the spider find its direction as well as the distance of its prey or threat. As a nocturnal species, the eye can see the platelets reflect light and the spider can see it in dim light. When the platen shows eyes light and the spider is illuminated at night.
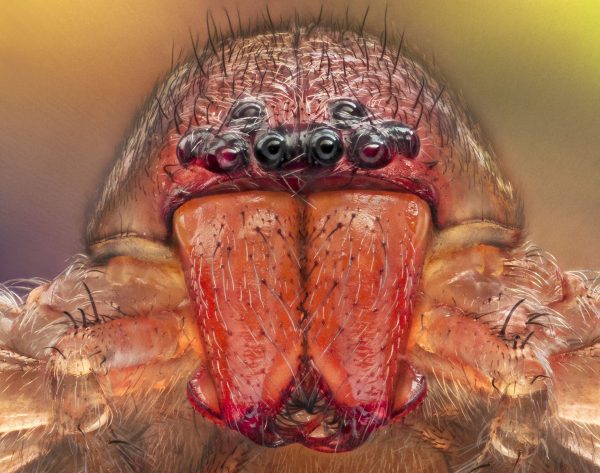
In some species, all eight eyes are located in front.
Use of spider eyes
Arachnologists use the spider’s eye to help classify and identify spiders . Since 99% of spiders have eight eyes and the number of eyes can vary within only one member of a species, the arrangement and shape of the eyes is often more helpful than the number. Even so, the details of the spider’s legs and spinnerets are more useful for identification.
- Eight-Eyes: The day active jumping spider (Salticidae), flower spider (crab spider), weaver ORB (Araneidae), spider web weaver (Theridiidae), and wolf spider are eight-eyed common spiders (Lycosidae).
- Six-Eyes: Several spider families have six-eyed species. These include some of the recluse spiders (Sicariidae), spitting spiders (Scytodidae), and cellar spiders (Pholcidae).
- Four Eyes: A spider belonging to the family Symphytognathidae and some spiders of the Nesticidae family have four eyes.
- Two eyes: Only spiders belonging to the family Caponiidae have two eyes.
- Trace or No Eye: A species that live exclusively in an underground cavern that can lose sight. These spiders generally have 6-8 eyes in different habitats and belong to the family.
The structure and biology of the spider
they are very interesting and are terrestrial creatures that have not been fully explored, so treat them with disgust, but in vain. Many call them insects, but they are not. Spiders are ancient arthropods.
In all spiders, the body consists of an abdomen, a cephalothorax, four pairs of feet and a rotating device. However, how many eyes a spider has is a separate question. It must be said that the lifespan of these creatures reaches 30 years, and most of them do not die from natural causes. The smallest spiders are no more than 0.5 mm in size, and the largest ones reach almost 30 cm. Today, about 42,000 species of spiders live, and new spiders are constantly being discovered, with more than 1,000 additional fossil species.
Features of arachnid vision
Various species groups of this class have adapted well. For many people, the main role is not the eyes, but the areas of increased sensitivity on the surface of the body. In particular, there are a lot of tactile hairs on the jointed legs and soles (leg tentacles) that are responsible for movement.
Many arachnids are weaving capture webs. With the smallest vibrations of the thread, they learn about the prey they encountered. Visual perception is less important. Species that lead a nomadic lifestyle and hunt without webs have a more advanced vision. To wander around unfamiliar terrain, you need to be able to distinguish between the surrounding reality.
However, their visual systems are also incomparable to the “opticals” of advanced insects. The scorpion’s eye (pictured below) is no different in the complexity of the device or in the characteristics of color rendering. It is believed that representatives of this suborder see something worse than spiders and can distinguish their kind only at a distance of a few centimeters.
The simple and complex vision of arthropods
Insect vision is the most advanced. In this regard, the eyes of arachnids are often called simple. In representatives of the development of insects, such as bees, dragonflies, and flies, compound eyes have a lateral structure. The structural unit of vision is the ommatidia. In fact, complex optical systems are made up of them. They are placed side by side to form a visual complex. The ommatidium consists of a biconvex lens (cornea), under which there is a transparent cone with similar properties to the lens.
Below is a layer of cells (retina) that can detect light rays. They connect to nerve endings that carry signals to the brain. Information is received individually from each ommatidium. As a result, the picture consists of many dots and resembles a mosaic image.
There are many such things in Paris. Structural elements reach 4 thousand in each eye. In this regard, there are up to 28,000 more developed dragonflies. Is it known that several pairs of scorpions in arachnids have a complex structure? There is no complex visual system. It is represented by several individually located ommatidial eyes. Also, one of the larger pairs is considered the main pair. The rest (up to 5 pairs) are on the sides and are considered auxiliary.
The simpler lateral eye (stemma) is found in insect larvae. Moving to the highest stage of development, the visual system becomes more complex. Other types of simplified eyes (dorsal) are not “born again” but remain at the same level in adults. Ommatidium is not formed (there are no cones and lenses). The light-receiving cells are located under the cornea. The lower one is a layer of pigments connected to the nerve endings.
Scorpio: lifestyle
Most often found in local tropical climates… some species are round, but the majority are still nocturnal hunters. They prefer to hide from hot heat during this period, hiding in stones, stumbling blocks, and other secluded places.
This is partly due to incomplete vision. They can only notice the danger at close range and have better adapted to hunting at night. However, this is not just due to the specific function of vision. It does not matter how many eyes the scorpions have (photo below)-they do not play a decisive role in catching prey. It is believed that the main advantage of an accurate attack is the sensitive sensor of the foot.
The circular posture of the legs gives the scorpion the opportunity to feel the smallest vibrations of the soil in all directions. The speed of propagation of these signals (a signal that the nearby leg feels earlier) determines the exact location of the victim. The eyes play a second role here. It is known that if the victim is separated from the scorpion with obstacles in the form of a slender gap, it cannot be attacked even at close range. In this case, soil signals from the movement of the prey to the sensitive legs do not reach.
The habitats and features of life have changed significantly and the appearance of this creature. Not only are the overall size of the body and each part different, but the number of eyes is different. Regardless of the total number, they all have a simple structure.
How many eyes do scorpions have and where are they on the body? Some species have adapted to live in pairs. The maximum number is 12 simple eyes. Also, a pair of them (obviously larger) are in the center and play the main role. The rest are on the sides and below the perimeter.
The scorpion, holding the victim with front tongs, is lifted overhead and pierced with the sting tip of the tail. How many eyes do scorpions have to control this process? Perhaps the upper steam is responsible for this to some extent. Whether a simple additional eye is a complication of the visual system (developed for improvement) or a simplification (there was no time to completely atrophy), it cannot be established with certainty.
Spider hits are known in both sciences- there are only about 42,000 modern species and more than a thousand arachnid fossils. Not only land, but also water, predators, vegetarians with rare exceptions, harmless and fatal to humans, lived on Earth for more than 100 million years and is widespread everywhere. Spiders are as interesting as a few insects. Unique external structure … This is primarily related to the organs of vision. Therefore, the question of how many eyes a spider has is interesting.
How many eyes does Spider have according to experts
Zoo ophthalmologists (experts in the field of animal vision) do not give a definite answer when asked how many eyes a spider has. In fact, the number of eyes of a spider varies by species.
However, it is still known how many eyes most spider species-4 pair. However, the owners of 12 (!) organs are known. In the course of evolution, nature left spiders with the organs of vision and powerful powers necessary for survival and reproduction. Regarding the power of vision, at the opposite poles, there are cave spiders (almost blind) and jumping spiders, whose visual power is equal to human power and at the same time, as proven, can distinguish colors.
Type of eye
In principle, eyes located in two rows have different functions. The so-called medial, aka front pair, is called the main eye. All other organs of vision are called collateral. Unlike insects with so-called multifaceted eyes, in which individual parts of the eye perform their functions, in spiders, the role of such faces is played by individual eyes. With the secondary eye, for example, the main task is to warn the owner of the impending danger.
The power of sight
The main eye of a spider can see even things that a person cannot distinguish. In particular, the sensitivity of these organisms to ultraviolet light has been demonstrated. This ability, unlike other representatives of arachnids, is owned by about 6 thousand species of jumping spiders, which, unlike representatives of other arachnids, prefer to actively hunt, on the contrary, without waiting for their victims in ambush.
Weak eyes are owned by snake spiders that catch their prey with the help of cobwebs. Their vision allows them to record the movement of relatively large objects (moths, flies), allowing them to respond to changes in the direction and intensity of light.
Eye features
Scientists have determined that all eyes function as one organ, no matter how many eyes a spider has (spider, crab spider, sand spider, or other species of this invertebrate). First, the presence of a potential victim (fly) is determined by the back or lateral eye. This occurs at the distance between the spider and the fly (at least 20-25 cm). Next the main eye, to which the main focus is transmitted, works. It is they who decide that the spider has the desired hunting target, not foreign objects.
So, the answer to the question of how many eyes a spider has is, which spider and in what habitat do you live in? Only after determining these parameters can you give an accurate answer to your question.
Habitat and Habitat
Spiders live all over the globe , but in warmer regions there are the most species. Almost all spiders are terrestrial animals. The exception is the silver spider that lives in the water. Many spider species hunt on water surfaces. Some spiders build nests, shelters, and burrows, while others do not have permanent habitat. In most cases, spiders are nocturnal animals.
Arachnida Spider
Arachnida is a type of arthropod that includes spiders, ticks, scorpions, and other lesser-known subtypes of chelicerae. Today, according to scientists, more than 100,000 species of arachnid live on Earth. Arachnids have two main body parts (head-thorax and abdomen) and four pairs of legs. Arachnids differ from insects in that they do not have wings and antennas.
In some spells of arachnids, for example, ticks and ricinuré, there are only three pairs of legs in the larval stage and a fourth in the nymph stage. Arachnids have exoskeletons that are shed periodically to allow animals to grow. In addition to the four pairs of legs, there are two pairs of additional appendages (chelicerae and pedipalps) that are used for various purposes, such as feeding, defense, movement, reproduction, or environmental awareness. Some species (especially ticks) inhabit fresh and salt water, but most species of arachnids are terrestrial animals.
Structure of Arachnids
In the internal structure of arachnids secrete nerves, respiratory, digestive, excretory, reproductive, special toxic and rotating organs. The organization of the nervous system is relatively complex and of a different type … its main feature is the brain with abdominal nerve chains and anterior and posterior parts.
The respiratory organs are the organs and lung sacs of spiders, representatives of other orders may have an organ that opens in the lower part of the abdomen with a respiratory opening or exclusively a lung sac. The trachea is a tube that permeates the animal’s body and is suitable for air gas exchange.
The digestive system consists of the esophagus, stomach and back intestine, ending with the excretory cavity. The ducts of the fecal Malpighian glands flow into the excretory cavity. All arachnids are rational, fertilization is internal, and development is direct. Most species are ovate and some are viviparous. Many arachnids have venom and/or arachnoid glands. The latter secretes a liquid, pulls it into the thread, and quickly hardens. Spiders make fishing nets from their webs or line up burrows.
Spider species
Scientists have described more than 42,000 species of spiders. About 2900 species are known on the territory of the CIS countries. Let’s consider several types.
- Tarantula turquoise (lat.Chromatopelma cyaneopubescens)-one of the most colorful and beautiful spiders in color. The tarantula’s abdomen is reddish-orange, its limbs are bright blue, and its carapace is green. The size of the tarantula is 6-7 cm, the length of the legs is up to 15 cm, and the spider’s homeland is Venezuela, but this spider is found in Asian countries and in the African continent … despite being a tarantula, the given view spider does not bite, but throws only special hair on the abdomen, a serious danger The same is true if this occurs. In humans, hair is not dangerous, but it causes minor burns to the skin with an effect similar to that of nettle burns. Surprisingly, female chromosomes are longer livers compared to males. The female spider has a lifespan of 10-12 years and males only 2-3 years.
- The flower spider (lat. Misumena vatia) belongs to the family of sidewalk spiders (Thomisidae). Colors range from completely white to bright lemon, pink or green. Male spiders are small, 4-5 mm long, and females 1-1.2 cm. Flower spiders are found in the United States, Japan, and Alaska, distributed throughout European territories (except Iceland). Since spiders eat the juice of butterflies and bees caught in “hug”, they live in open spaces rich in flowering herbs.
- Grammostola pulchra (lat.Grammostola Pulchra)-a type of tarantula spiderlives only in the natural environment of Uruguay and southern Brazil. It is a fairly massive spider, reaching 8-11 cm in size, with a dark color and a characteristic “metallic” fur luster. Essentially, he prefers to live among the roots of plants, but he doesn’t actually dig his own mink. Pulchra often becomes a pet among connoisseurs of exotic pets.
- Argiope Brunnich or wasp spider (lat.Argiope bruennichi)-a spider with an unusual color of the body and limbs-yellow-black-white strips got its name. In fact, males of wasp spiders are not so bright and are inferior in size to females. The “young lady” is 2.5cm tall and the feet reach 4cm, but males rarely grow more than 7mm long. This species is widespread in Europe, Asia and southern Russia, the Volga region and North Africa. The argiope spider lives in grassy meadows at the edge of the forest. Argiopa’s web is so strong that it is difficult to break and stretch only when pressure is applied.
- Hunter limbs (Latin Dolomedes fimbriatus) are widespread in the Eurasian continent and occur along the shores of reservoirs with stagnant or very slow flowing water. Often settles in swamps, shady forests or gardens. High humidity … The length of the body of the female of the limping hunter varies from 14 mm to 22 mm, and the males are smaller and rarely larger than 13 mm. The color of the spiders of this species is usually tan or almost black, with bright yellow or white stripes on the sides of the abdomen.
- Apulian tarantula ( Latin Lycosidae)-a spider species belonging to the family of the wolf spider (Latin Lycosidae). It inhabits vast areas of southern Europe. Commonly found in Italy and Spain, it digs a hole 0.5 m deep in Portugal. The size of the tarantula is impressive-up to 7 cm long, individuals are usually red, in less often-brown tones, with several horizontal stripes on the body bright color and one vertical.
- Spike sphere spider or “horn spider” (lat. Gasteracantha cancriformis) is distributed in the tropical and subtropical regions of the southern United States. Central America, the Philippines, and Australia. Females are 5-9 mm in size and reach 10-13 mm in width. Males are 2-3 mm long. The legs of a spiny spider are short and have 6 spines along the edge of the abdomen. The color of the spider is very bright-white, yellow, red, and black. There are black spots on the abdomen.
- Peacock spider (lat. Maratus Volans). There are all kinds of colors for this spider: red, blue, blue, green, and yellow. Females are lighter in color. Adults grow to 4-5 mm in size. Males attract females with beautiful clothes. Peacock spiders live in Australia-Queensland and New South Wales.
- A smiling spider (lat theridion grallator) or a spider with a happy face is completely harmless to humans. This unusual spider lives in the Hawaiian Islands. The body length is 5mm. The color of the spider can vary, including pale, yellow, orange, and blue. This species feeds on small lugworms, and the individual’s bright color helps to confuse enemies, especially birds.
- The black widow (lat.Latrodectus mactans) is a very dangerous and venomous species of spider. It is also found in Australia, North America, and Russia. Females reach 1 cm in size, and males are much smaller. The body of a black widow is black, with characteristic red hourglass-shaped spots on the abdomen. The males are brown and have white stripes. Being bitten by a black widow is fatal.
- Karakurt (lat. Latrodectus tredecimguttatus) is a species of deadly tarantula of the genus Black Widow. Female karakurt is 10-20 mm, males are much smaller and 4-7 mm in size. There are 13 red spots on the abdomen of this scary spider. In some species, spots have a border. Some sexually mature individuals have spotless and completely black glowing bodies. Karakurt lives in Kyrgyzstan, Astrakhan region, the country. Central Asia, southern Russia, Ukraine, Black Sea and Azov regions, southern Europe, and North Africa. Also, karakurt can be found in the Saratov region, the Volgograd region, the Orenburg region, and the Kurgan region, and south of the Urals.
What does Spider eats?
With the exception of some ticks, all arachnids are predators, usually eat insects and other small animals, and are usually caught alive. Only the liquid tissue of the prey is sucked out (external digestion), and solid particles are not swallowed. Most arachnids are armed with venom glands but can be dangerous for humans.
The most poisonous species of spiders in the United States are “Black Widow” ( Latrodectus Mactan ) and those close to him; Their bites are very painful and sometimes fatal. Some large tropical bird eaters are considered dangerous, but the bites of representatives of this group living in the southern and western United States are mostly similar to those of wasps. An extremely poisonous scorpion carries a painful sting with a stinging sting at the tip of the tail. Contrary to popular belief, large phones found in the southwestern United States are not toxic. Some ticks carry pathogens such as Rocky Mountain Fever.
Like insects, arachnids live everywhere. They are widespread up to the limit of the altitude of life in mountains up to 80 ° N, and are also found in the air at a height of thousands of meters above the ground and carried by the wind along with fragments of a spider web.
Nutrition
The anterior part of the arachnid intestine (pharynx) with strong muscles acts as a pump. The midgut usually has lateral protrusions that increase its capacity. The liver secret and salivary gland arachnid break down proteins. It is injected into the body of the killed prey to make its contents semi-liquid and then absorbed through the pharynx (this method is intestinal digestion ).
Spider breeding
As spiders grow, they sometimes peel off a hard chitinous bark and grow into a new bark. You can shed up to 10 times in a lifetime. Spiders are heterosexual, and females are much larger than males. During the mating season that lasts from mid-central to early spring in males, males fill sperm into bulbs at the tip of their feet and set out in search of females. After making a “mating dance” and fertilization, the male spider quickly retreats and dies shortly after.
After two and a half months, the female spider lays eggs, and after 35 days a small spider appears, living before the first molting of the web. Females mature sexually at the age of 3-5.
Of the spiders, only poisonous ones are dangerous to humans. On the territory of the CIS countries, there are species such as karakurt or black widow. Timely infusion of special serums will not result in a bite.
How do spiders weave a web?
All spiders weave a web. It is used not only for hunting but also for movement, it creates a smooth wall in the burrow and creates an egg pocket. Most spiders have four holes in their abdomen called ‘death’. When a spider unwinds its web, it appears to consist of a single strand.
In fact, one spider web consists of many thin threads that are attached to each other. Special liquid … When this liquid enters the air, it hardens. Many spiders use cobweb threads to return to their burrows.
Different types of spiders have different webs. It can be sticky, dry or elastic. The webs are so strong that some spiders use them to fly for miles. Spiders can eat webs and start weaving new webs when they are no longer needed.
Male spiders are smaller than female spiders. When mating, males need to be very careful. The female does not accept courtship and simply decides to eat her partner. Even if mating occurs, females can attack later, so males generally try to retire sooner. But this doesn’t happen very often.
Spiders lay 2 to 1000 eggs, depending on the species. Almost all females weave webs, place their eggs in a “blanket,” and then hang their pockets in a safe place to protect them. When small spiders hatch, they often stay inside the bag to grow a little more. Some females immediately neglect the egg sac and do not pour.
What is arachnophobia?
Arachnophobia is a way to call the fear of arachnids, it is a completely new disease and manifests itself as Special circumstances and necrophobia (typically fear of insects). Since ancient times, humans have experienced fear of the unknown. Fear of insects at an instinctive level is inherent in everyone. We all fear things that seem unknown to us at first. Someone who has learned more about spiders is not afraid of spiders and realizes the harmlessness of most species. And if someone remains in insect aversion for a long time, spiders begin to appear to pose huge dangers and threats.
Arachnophobia is very common and affects almost half of all women and a fifth of men. Scientists suggest that the fear of spiders is very common in women due to the fact that spiders are more sensitive to the senses of touch and their skin is more sensitive. The feeling of being touched by insects leaves a greater impression on them and arouses fear.
Arachnophobia is often combined in a person with other fears.
- myrmecophobia-fear of ants;
- bathmophobia-fear of cockroaches;
- lepidopterophobia-fear of butterflies.
All of these fears have the same underlying cause and are often not shared, but they generalize to one disease called insect phobia (insect phobia is called insect phobia in a different way).
Phobia reasons
Arachnophobia is a very common disease in The modern world this is due to a large number of city dwellers. Since this part of the population has little contact with spiders, it is not always possible to distinguish dangerous species from harmless ones.
At the current level of knowledge about spiders, the practical importance of spiders actually boils down to the harm caused by some form of a poisonous bite. However, many spiders are undoubtedly useful as pest exterminators, but this role has not yet been accurately evaluated. There are also some prospects for the technical use of spiders.
The biological significance of spider venom is reduced primarily to killing prey, so venom is generally toxic to insects. There are few spider species whose venom strongly affects warm-blooded animals, but some are very dangerous to humans and livestock. Tarantula depends on the nature of the poisoning. Some poisons primarily cause local necrotic reactions, that is, necrosis and destruction of the skin and deeper tissues at the site of the bite. Other people’s poisons have a strong effect on the entire organism, especially the nervous system.
Although some large tropical bird bites and deaths of humans and animals have been recorded more than once, the toxicity of most spiders has not been accurately determined. Among them, Phormic-topics in poisonous lines contain enough poison to kill 20 rats. The Bushmen mixed spider venom from this genus in South Africa with the juice of Amaryllis bulbs and used it to poison arrows.
The venom of the spider Mastophora gasteracanthoi-des (Araneidae family) found in Peru has a strong necrotic effect and infects people who care for vineyards. The bite may experience sharp pain, severe swelling, and further destruction of tissue in the affected area, leading to exposure. Internal organs … The deaths mentioned in several cases are probably due to secondary wound infection. A similar picture is caused by the bite of the Brazilian Lycosa gar-Toria (Lycosidae family).
The general effect on the body is characteristic of the Brazilian poison Ctenus nigrivent-ris (Ctenidae family), which is dangerous to bite. Even more dangerous is the small (4 to 5 mm) horse Dendjyphantes noxious found in Bolivia. Its bite causes inflammation and severe pain, as in red hot iron. Blood appears in the urine and dies a few hours later.
Very strong common behavior It possesses the venom of a spider of the genus Latrodectus (family Theridiidae), which includes karakurt (L. tredecimguttatus) found in our desert. Steppe zones are common in Central Asia, the Caucasus, the Crimean Peninsula, Iran, Afghanistan, and coastal areas. Mediterranean … In the United States, L. mactans, a venomous species of the same genus, are widespread. L. mactans received the name “Black Widow” there. Other species are found in tropical countries.
The scariest spider in the world
Yellow (gold) sac
Its main habitat is Europe. Do not grow more than 1 cm in volume. The color is golden and translucent. Yellowsock ‘s unexplained appearance and small size make it possible to crawl around in residential buildings for quite some time while not being noticed. In natural conditions, he always built a house that looks like a piping bag. A necrotic wound is provided that causes severe pain by being bitten by this animal. These symptoms are very similar to the action of the poison of a violin spider. Saki is vulnerable to self-defense and only attacks when he feels danger with him.
Wandering Brazilian spider
They got such a nickname for a reason. -In search of food, constantly changing positions. This spider lives mainly in South America. This species is considered one of the most dangerous. Wanderers already have a very impressive volume of about 10 cm. The amount of poison contained in one individual is enough to kill 225 mice. The antidote to it already exists. But his bite in some way will lead the human body to a serious allergic reaction.
Wanderer is difficult to find in nature because of its inconspicuous sand color. It sounds funny, but he got the nickname “banana” because it’s usually found in banana baskets. The wanderer chooses prey that are much larger than their size. It can be a bird, a lizard or another spider.
Brown recluse (violin)
This view poses a very great danger to humans , as the poison spreads throughout the body in just one day after a bite. If the victim is not hospitalized on time, the consequences will be very disastrous. These spiders, like the Yellow Sak, do not attack first unless they feel threatened to themselves, but in any case, contact should be avoided.
Hermit grows up to 2 cm and usually hides in dry, dark places. It can be found in California and other US states. This species can be distinguished by its characteristic shaggy “antenna”, and unlike most spiders, it has only 3 pairs of eyes. 8 eyes.
Black widow
As mentioned earlier, the most dangerous spider on earth is a female black widow … its venom is deadly. In size, she, like a hermit, can reach up to 2 cm. Black, with small spots on the back. And because the widow takes the life of a partner after mating. By comparison, the poison rattlesnake is 15 times less dangerous than the venom of a terrible arthropod. The bite in females is very dangerous and can lead to death if the victim does not get the injection even after 30 minutes. Black widows do not only live in one country but can be found in deserts around the world.
Tarantula (Tarantula)
Found in desert and steppe areas where they dig deep holes themselves. Nature has endowed this species with a unique beauty. The body is gray, brown and orange. Sometimes striped objects are found. Unlike the hermit, the tarantula is completely fur. They usually grow up to 3-4 cm and eat small birds, so they have a second name-tarantula. They hunt at night thanks to their excellent night vision.
Water spider
Their habitual home is a pond in North Asia and Europe. Does not grow more than 1.7 cm. They have such a name because they swim very well. They live underwater in the same place, seaweed, weave nets. They eat a variety of small aquatic animals. Its poison is absolutely not dangerous to humans, but it looks scary.
Spider crab
There are over three thousand species in the world. They are large and most diverse in color and strangely similar to their habitat. Like a chameleon, it can blend into almost any surface, such as green or sandy terrain.
Roots in three places:
- Southern europe
- North America
Spider crabs do not pose a strong threat to humans, but they are less afraid than others because they are often mistaken for poisonous hermits. Dangerous species …they got their name in honor of the crabs because they look similar and very mobile like this decapod crustacean. Like Brazilian spiders, they prefer to hunt without weaving webs. I can only move back and sideways.
Wall tegenaria
A rather rare species today, but the largest view in Europe. Its dimensions range from 12.5 to 16 cm on the straight limb.
The residence of this spider is as follows:
- Uruguay
- North africa
- Central asia
You can stumble upon Tegenaria in a cave or in an old building. In England, this spider was called “Cardinal”. According to legend, seeing this spider, where Cardinal Woolsey once lived, experienced a very strong horror. Tegenari moves very fast. The structure of the spider web is very thick, so the insects that meet it rarely have a chance of salvation.
Cerbal Arabia
First found in Israel at the end of 2010 … can be found in the dunes. It has a large, silver-gray body with characteristic stripes on the legs. The coloring is very scary. To date, little is known about their lifestyle. According to scientists, they are especially active in the hottest season.
Giant baboon spider
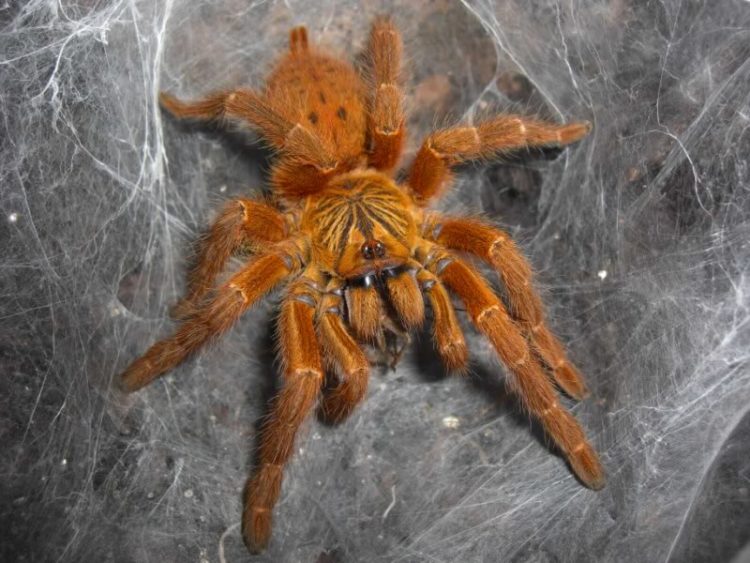

Has a second name -Red Cameroon … The length of the body is 10 cm, the legs are about 20 cm, usually the spider reaches 30 cm. The baboon spider belongs to the family Tarantula and loves subtropical forests.
Quite a lot of colors predominate in coloring.
- Orange
- grey
- Brown
- black
His legs, unlike the calf, are covered with small fur. The diet is large enough and can eat insects, but it does not give up mice and other similar animals. Inject killing poison into the prey.
Of all the above, the title of the deadliest spider on Earth was designated by “Black Widow”. The titles I fear most undoubtedly belong to the wandering Brazilian spider.
Spiders surround us everywhere. So it’s important to know which spiders are safe and which ones to avoid.
Spiders are one of the oldest inhabitants of the planet known during the Devonian and Carboniferous periods. It is said to have appeared about 400 million years ago. Creatures of the Paleozoic era had unique spider web devices, but they were more primitive. Their habitat is the widest all over the planet except Antarctica.
Spider Science: What do you call it?
Araneology is the science of spiders, which is part of zoology-spiderology. Macroesthetics studies arthropods, invertebrates, and arachnids. The name comes from ancient Greek.
In addition, spider aesthetics are a technique that predicts the weather by observing the behavior of a spider.
Spider-what is it: types
Researchers know about 42,000 species of spiders. Spiders can be divided into three large suborders, mainly differing in the structure of the jaw, more precisely, the position of the chelicerae relative to the longitudinal axis of the body.
Orthognathic suborder
More often, representatives of this suborder are called mygalomorphs. It is characterized by thick hairs, large size and primitive structure of the jaw-the claws face down and grows only on the upper jaw. The respiratory system is represented by the lung sac.
Most mygalomorphs live in warm climates. Oysters make their own underground.
Orthognathic includes:
- tarantula
- Funnel spider
- ctenisides
- Spider-excavator

Suborder Araneomorpha
Almost all spider species known to naturalists are the large group Labidognatha or Araneomorpha. The difference is that both jaws have claws. The respiratory system is represented by an organ.
Types of spiders that catch prey without a net:
- Spider crab
- Jumping spider
- Wolf spider
Types of web spiders:
- linifed spider
- Snake spider
- Funnel spider or brownie
- Long-legged spider
- Old web spider
Some araneomorphic spiders are unable to produce cribellum, a substance that spiders produce durability. Spider web, and the people that produce it.
Suborder Mesothelae
Lifistiomorphic spiders are distinguished by the fact that the chelicerae are spaced sideways and do not face downwards. This position is considered more evolutionarily advanced. However, this suborder is considered the most primitive, and traces of it have been found in Carboniferous sediments. The spider has an archaic lung sac, and 4 pairs of arachnoid warts that have not yet moved to the ends of the abdomen. They live in dirt holes closed with lids. The signal thread is emitted from the mink. One species prefers caves but creates spider webs on the walls.
These include:
- Spider arthropod
- Primitive spider arthrolicoside
- Primitive spider arthromygalide
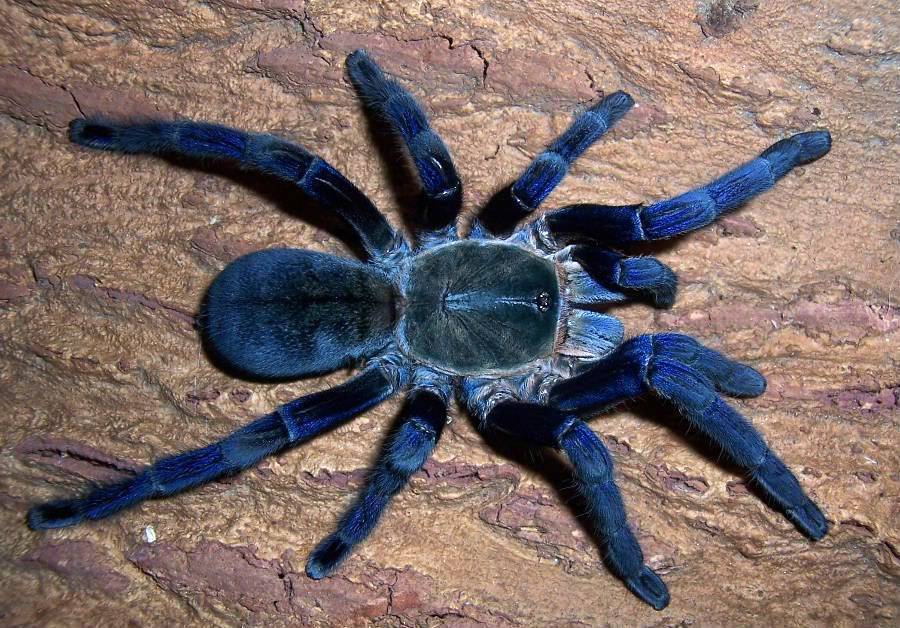

Spider: insect, animal or not?
Spiders belong to the type of animal-the order of arthropods in the type of spiders. Therefore, spiders are not insects, but animals.
Difference between spider and insect:
- Spiders have four pairs of legs and insects have three pairs.
- Spiders do not have the antenna characteristics of insects
- Many eyes, up to 12 pairs
- The spider’s body always consists of a cephalothorax and an abdomen.
- Some types of spiders are intelligent. They can distinguish strangers from themselves, protect their owners, feel the owner’s mood, and even dance to music. Unlike animals, no insect can do this.
Spider body structure
The spider body, covered with the outer skeleton of chitin, consists of two parts connected by small tubes.
- The cephalothorax is formed by the union of the head and chest.
- stomach
Cephalothorax
- The cephalothorax is divided into two parts: the head and the thorax by a groove. In the area of the bangs are the eyes and chin-chelicera. In most spiders, chelicerae face downwards and end with claws. Self-righteousness is in the claws.
- The lower part of the chin-the sole of the foot is used as a sole and a grabbing element. There is a mouth for sucking between the soles of the feet. For some sexually mature men, pedipalps is also a copulation device, symbiosis.
- Simple eyes are also found in the frontal area.
- Four pairs of articulated legs are also found in the cephalothorax in the thoracic region. Each spider’s leg has 7 segments. The last limb of each leg has two or more smooth or serrated claws.
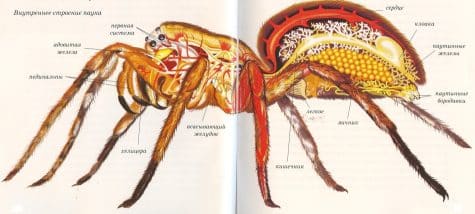
Stomach
- The abdomen can have a round, oval, angular, elongated, worm-shaped shape. There is a stigma in the abdomen-a breathing hole.
- In the lower part of the abdomen are spider warts with spider glands. The genital opening is located near the base of the abdomen. In females, it is surrounded by thick chitinous plates, and in males, the genital opening looks like a simple slit.
Spiders can grow up to 10 cm in size, their limbs can exceed 25 cm in length, all of which depend on the species. The smallest representative is only 0.4 mm.
The color, pattern depends on the structure of the scales and hair covering the body, the presence of pigments and the type of spider.
How many legs and limbs does a spider have?
- All spiders have four pairs of legs, located on the cephalothorax and are usually covered with hair.
- Each leg has a crescent-shaped hail saw. Between the toenails there is a sticky pad, which is a claw-like appendage.
- Web weaving spiders have secondary serrated claws that allow the spider to move freely along the web.
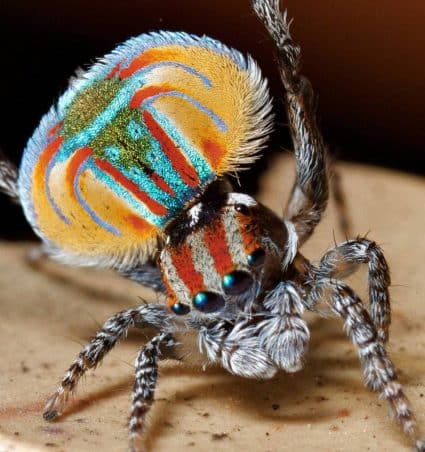

How many eyes does a spider have?
- It depends on the type. Some species have only two eyes and some have a maximum of 12. Most species have 8 eyes and are arranged in two rows.
- In any case, the two front eyes are the main eyes. They differ in structure from the other lateral eyes. They have muscles that move the retina and do not have a reflective cover. Also, the secondary eye is distinguished by the presence of light-sensitive retinal cells. The more they have, the sharper the spider’s vision will be.
- Some spiders can see colors just like humans. For example, a jumping spider. Night hunters, for example the Indian spider, have excellent vision not only at night, but also during the day. However, the wandering spider is best seen.
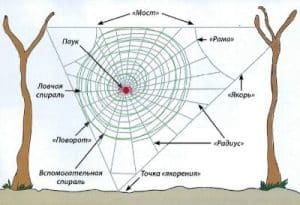
How do spiders weave a web?
The threads of the web consist of many thin threads that the spider adheres together with a special liquid that quickly hardens in the air. Thanks to this, the strength of the web has increased so that the spider will travel with it as the spider overcomes a distance of kilometers.
The web can be dry, sticky and elastic. It all depends on the purpose of the room.
Thread types for spider web:
- Cocoon
- Catching sticky threads
- For moving
- To obfuscate prey
- Screws for fasteners
The composition of the web depends on how you hunt. Spiders are weaved using threads that reflect the ultraviolet rays that most insects see. In addition, spiders weave ultraviolet reflective threads to look like flowers that reflect ultraviolet rays. Therefore, insects fly to the enchanting and sweet flowers and fall into the spider web.
Steps to weave the web:
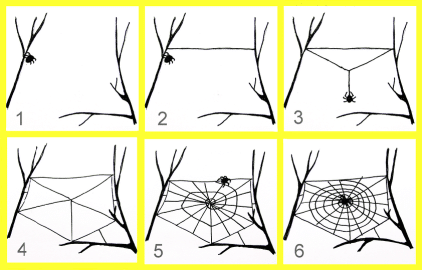
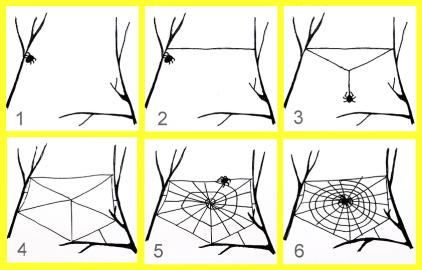
- The spider first unwinds the long thread. Such a thread is picked up by the air stream, runs to the nearest branch and sticks to it (Figs. 1, 2).
- Then another parallel free-hanging thread is woven. The spider moves to the center of this thread, pulled by its weight, and weaves another thread down until it finds the third support (Fig. 3).
- The spider attaches the thread to the support and gets a Y-shaped frame.
- Here are the typical contours and more radii (Fig. 4).
- At this radius, an auxiliary spiral is woven (Fig. 5). This whole frame is woven with non-sticky threads.
- Next, the spider weaves a second spiral from the edge toward the center of the web with a sticky thread.
Construction may take 1 to 2 hours.

How do spiders breed?
- Males generally differ in size from females (males are smaller), long legs, bright color, the presence of the soles of the paws that appear in males only during the last molting.
- First, the male weaves a special sperm web. Some types are limited to a few stretched threads. Then the spider applies a drop of sperm to the web, fills the pedipalps with sperm, and introduces the sperm to the woman as a semen reservoir. And he goes to the woman.
- Spiders look for females by smell. After finding a suitable female, the male begins to approach it carefully. If the female does not court, it can attack and eat spiders.
- When the female looks favorably at the male, the male begins to seduce the female. He does “wedding dance”, “jerky” with his feet and gets food. The spider, which has tied the female, carefully approaches her, touches it with the tip of the leg, then touches it with the sole of the foot and retreat. The male is also the “drum” of the substrate.
- If the female does not show aggression and does not “drum” herself, the male will approach it carefully and bring the sole of the foot to the female’s genital opening. The action lasts for a few seconds.
- Then the male runs away so that the female does not eat him. Although this rarely happens. Females can have multiple males in one season.
- After 6-10 weeks, the female squeezes a cocoon and lays 500 eggs. The female holds the cocoon between the chelicerae and carefully protects it. Spiders appear after 5 weeks.
How long does a common spider live?
Most spiders live for a year. However, some species, such as Grammostola pulchra of the tarantula spider, can live up to 35 years. And this applies only to females, and males also live for 2-3 years, even tarantula spiders.


Non-poisonous spiders: a list with names
There are no poisonous spiders at all. You need poison to paralyze and protect your victim.
However, the venom of most spiders you encounter is not dangerous. In some cases, it is too little that no one notices, or redness and swelling appear. Even in isolation, an allergy to spider venom can occur.
Frequent spiders that are safe for humans :
Common Haymaker spider … male size-up to 7 mm, female-up to 9 mm. The legs are long. They hunt in the dark. They love to flock to look like a bundle of wool. Weave a non-sticky web. Surprise your enemies with an unpleasant smell.

More than 5 thousand species. It’s a small size 5-6mm spider that likes to bask in the sun and rises perfectly over the glass. A good jumper can jump up to 20 cm. The web is not squeezed, attacks by jumping, and has excellent eyesight.

More than 1,000 species. The size is up to 25 mm-female, and up to 10 mm-male. There are several white spots on the abdomen, forming a cross. They hunt using round fishing nets up to 1.5 m in diameter.

Size up to 10mm. Hunts in an ambush immediately capture the victim and paralyze it with poison. We do not create a network. Has a camouflage-if necessary, the color changes from dark yellow to white. Hunting on the bark is brown, and the leaves are variegated.

House spiders or funnel spiders, are the most famous and widespread. Weaving a web in a secluded place: ceiling, corners, behind wardrobes. Males up to 10 mm, females up to 12 mm, slightly larger. The color is yellowish-gray with brown spots.

Females are up to 10 mm in size, and males are slightly smaller. The color is pale yellow and has a green color. In the lower part of the abdomen there are two bright stripes elongated in the form of seeds. They make a circular net with large “holes” designed for mosquitoes with long legs. The web was built near water and knows how to run on water.

Male size-up to 16 mm, female-up to 12 mm. A rare spider that lives in poor fresh water. You can swim. The abdomen is covered with hair to trap air, so the spider appears “silver” in the water. Air-filled “bells” are woven into the water, and they live there. It rests, leaves supplies, and feeds on caught prey.

Bird-eating spider (tarantula). Large, leg length up to 20 cm. They have a beautiful variety of colors. Weaving the web. Some species are completely harmless to humans. In other species of bite, swelling, redness, itching, fever, and muscle cramps may appear. No deaths were reported. They are most often kept at home, and females of some species live up to the age of 35. They are very unpretentious in care. Bird eaters can also be trained.

Top 10 most dangerous, poisonous and deadly spiders on Earth: list of names
People living in the tropics and subtropics of South America are the most dangerous spiders, according to the Guinness Book of Records. The size of the spider is 10-12.5 cm, it is fast, active, does not weave a web, it constantly moves in search of prey. I like bananas. It eats other spiders, insects, lizards, and birds.
In case of danger, stand up and show your fangs. Poison is deadly to weakened people, children. Without help, death from bites in some individuals can occur within 20-30 minutes. Healthy adults usually have severe allergic reactions.
Its habitat is the deserts of South America and Africa. They can last as long as a year without food and water. The maximum size considering the length of the leg is 5 cm.
When hunting, they are buried in the sand and come close to attack from cover. Poison is a hemolytic necrotic toxin that dilutes the blood and causes tissue breakdown. The victim dies from internal bleeding. No antidote has been created, but people rarely die.
Habitat-Australia, within a 100 km radius of Sydney. Size-up to 5 cm. Live and hunt in stumps, under stones, in trees or in open spaces. This poison is not dangerous for most mammals, but it is lethal to humans and primates.
Spider is in danger and shows fangs. When bitten, it bites the victim’s body and is bitten several times in succession. It is also difficult to peel off. Poison is dangerous due to its large amount. First, the state of health worsens: nausea, vomiting, sweating. Then-decreases arterial pressure and blood circulation is disturbed, and eventually, the respiratory system fails.
The most known species … habitat-Mexico, the United States, southern Canada, New Zealand … they prefer to live in deserts and steppes. Females can be up to 1 cm in size, and females are more dangerous than males. If bitten by a female, the antidote should be administered within 30 seconds.
Spider venom is 15 times stronger than venom Rattlesnake. The bite site heals for up to 3 months. The bite is characterized by acute pain, and after an hour it spreads all over the body, causing convulsions. Difficulty breathing, vomiting, sweating, headache, limb numbness, fever.
Outwardly, it looks like a black widow. Originally lived in Australia, but now it has spread all over the world except for plays. It is up to 1 cm in size and eats insects, flies, cockroaches, and even lizards.
The poison cannot kill a person, but after a bite you feel pain, convulsions, nausea, increased sweating, and general weakness.
6. Karakurt- “Black Bug”
From a kind of black widow, living in the steppes and deserts of Russia. Males up to 0.7 cm in size and females up to 2 cm. The most dangerous is the poison of females with red dots on their abdomen.
The spider bite itself is barely noticeable, but after a few minutes a sharp pain is felt and gradually spreads throughout the body. Convulsions begin, a red rash appears, and the victim may feel unreasonable fear, depression. Without help, a bite can be fatal for 5 days.
The second name is the violin spider. Habitat-Northern Mexico, Southern United States, California. Males are 0.6 cm in size, females up to 20 cm and are not aggressive. Lives in a dark and dry place: attic, warehouse, closet.
The bite is almost numb. If the poison spreads all over your body within a day after being bitten, you begin to feel the effect of the poison. The temperature rises, nausea, rash, general pain, and tissue swelling appear. In 30%, tissue necrosis begins, sometimes organs are damaged, and only a few have been recorded.
Initially it only lived in South America (Chile), but now it also resides in North America, which is found in Europe and Australia. Abandoned Places: Lives in warehouses, piles of timber, attic. Eats insects and other spiders. Size, including feet-up to 4 cm.
The bite is painful and its strength resembles a cigarette burn. Poison has a necrotic effect. The victim feels excruciating pain. Kidney failure may develop. Treatment takes months and 1 in 10 people die.
9. Wolf Spider
Habitat-all over the world except Antarctica, but preferred warm country … They live under thickets, grassy meadows, forests near water sources, fallen leaves, stones. Size-up to 30 mm. They eat cicadas and bed bugs.
Bites from tropical species can cause prolonged pain, dizziness, swelling, severe itching, nausea, and a fast heart rate. Their poison is not lethal.
Terra fossa blonde
10. Terra Fossa Blonde
Then one of the largest spiders , the second name is Goliath tarantula. Body size-up to 9 cm, leg length-up to 25 cm. It feeds on toads, mice, small birds and snakes. Bites only in dangerous cases.
The poison has a paralytic effect. However, in humans, it is full of swelling and itching. When bitten by large animals and humans, poison is usually not injected. In case of danger, the tarantula irritates the mucous membrane by brushing its sharp hairs off the back.
There are many dangerous spiders, but they rarely attack. Attacks are usually related to defense, avoiding ordinary life spiders and preferring secluded places for life. There are few deaths, but caution is always required when handling these animals.






